DWG Converter, a crucial tool in the world of Computer-Aided Design (CAD), enables seamless file conversion between various formats. DWG, the native file format for AutoCAD, often needs to be transformed into other formats for collaboration, data sharing, or compatibility with different software. This conversion process is essential for architects, engineers, and designers who work with CAD models on a daily basis.
Table of Contents
From simple drawings to complex 3D models, DWG converters play a vital role in facilitating efficient workflows and ensuring interoperability between diverse CAD applications. They bridge the gap between different software platforms, enabling users to share their designs with colleagues, clients, or other stakeholders who may not have access to the original CAD software.
Introduction to DWG Converter
DWG is a file format commonly used in computer-aided design (CAD) applications. Developed by Autodesk, it is the native file format for AutoCAD, a popular software for creating and editing 2D and 3D drawings. DWG files contain various data, including geometric shapes, lines, curves, text, and other design elements. The significance of DWG lies in its ability to store complex design information in a format that can be shared and accessed by different CAD software programs.
A DWG converter is a software tool that allows you to transform DWG files into other file formats, such as PDF, DXF, SVG, and more. This conversion process is essential for various reasons, including:
DWG Converter: Purpose and Benefits
DWG converters play a crucial role in enabling seamless data exchange between different CAD programs and platforms. They offer several advantages, including:
- Compatibility: DWG converters bridge the gap between different CAD software applications, allowing users to share and collaborate on designs regardless of the software they use. For instance, a user working with AutoCAD can convert their DWG files to DXF format, which is compatible with other CAD programs like BricsCAD or DraftSight.
- Accessibility: DWG converters make CAD designs accessible to individuals who may not have access to specialized CAD software. By converting DWG files to more widely supported formats like PDF, users can view and share design information without requiring specific software licenses.
- Data Preservation: DWG converters ensure the preservation of design data by converting files to formats that are less susceptible to version incompatibility issues. This is particularly important for long-term storage and archiving of CAD drawings.
- Simplified Sharing: DWG converters simplify the process of sharing CAD designs with stakeholders who may not have access to CAD software. By converting DWG files to formats like images (JPEG, PNG), users can easily share designs with clients, colleagues, or other parties.
Real-World Scenarios
DWG conversion is essential in numerous real-world scenarios, including:
- Architectural and Engineering Design: Architects and engineers often collaborate on projects using different CAD software. DWG converters enable them to share design files seamlessly, ensuring consistency and accuracy across different platforms.
- Manufacturing and Production: DWG files are frequently used in manufacturing and production processes. DWG converters facilitate the exchange of design information between different departments, such as engineering, design, and manufacturing, ensuring smooth production workflows.
- Construction and Building: DWG files are widely used in construction projects for creating floor plans, elevations, and other design documents. DWG converters allow contractors, subcontractors, and other stakeholders to access and share design information effectively.
- Education and Training: DWG converters are valuable tools in educational settings, enabling students to learn and practice CAD skills using different software programs and file formats.
DWG Conversion Processes
DWG conversion is the process of transforming a DWG file, a proprietary format used by Autodesk’s AutoCAD software, into another file format. This conversion is often necessary when sharing or utilizing CAD data with software that does not support the DWG format.
The conversion process involves several steps, including reading the DWG file, interpreting its contents, and then generating a new file in the target format. Different converters employ various methods to achieve this, each with its own strengths and limitations.
Conversion Methods
The choice of conversion method depends on the converter’s capabilities and the specific requirements of the conversion task. Some common methods include:
- Direct Conversion: This method directly translates the DWG file’s data into the target format. It is often the fastest and most efficient method, but it may not preserve all the original DWG file’s data and formatting, especially if the target format lacks certain features.
- Intermediate Format Conversion: This method involves converting the DWG file to an intermediate format, such as DXF, and then converting the intermediate file to the target format. This method can be more accurate than direct conversion, as it allows for more flexibility in data interpretation and processing. However, it can be slower and more complex.
- API-Based Conversion: Some converters utilize APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) provided by the target format’s software to directly generate the target file. This method offers high accuracy and preservation of data, but it requires the converter to have access to the target format’s API and may be limited to specific software applications.
Challenges and Limitations
DWG conversion can present challenges and limitations due to the complexity of the DWG format and the differences between file formats. Some common challenges include:
- Data Loss: Not all DWG data can be accurately converted to other formats, especially when dealing with complex geometries, custom objects, or specific AutoCAD settings. This can result in data loss or formatting inconsistencies in the converted file.
- Compatibility Issues: Different software applications may have varying levels of support for DWG file features and may interpret DWG data differently. This can lead to compatibility issues when opening or using the converted file in different software.
- Version Differences: DWG files can be saved in different versions of AutoCAD. Converters need to be able to handle these version differences and ensure accurate conversion of data across versions.
- Security Concerns: DWG files can contain sensitive data, and it is essential to use trusted and secure converters to protect this data during conversion.
Key Features of DWG Converters
Choosing the right DWG converter can be crucial for efficient and accurate conversion. Several key features can make a significant difference in your workflow and the quality of the converted files. Understanding these features can help you make an informed decision when selecting a DWG converter.
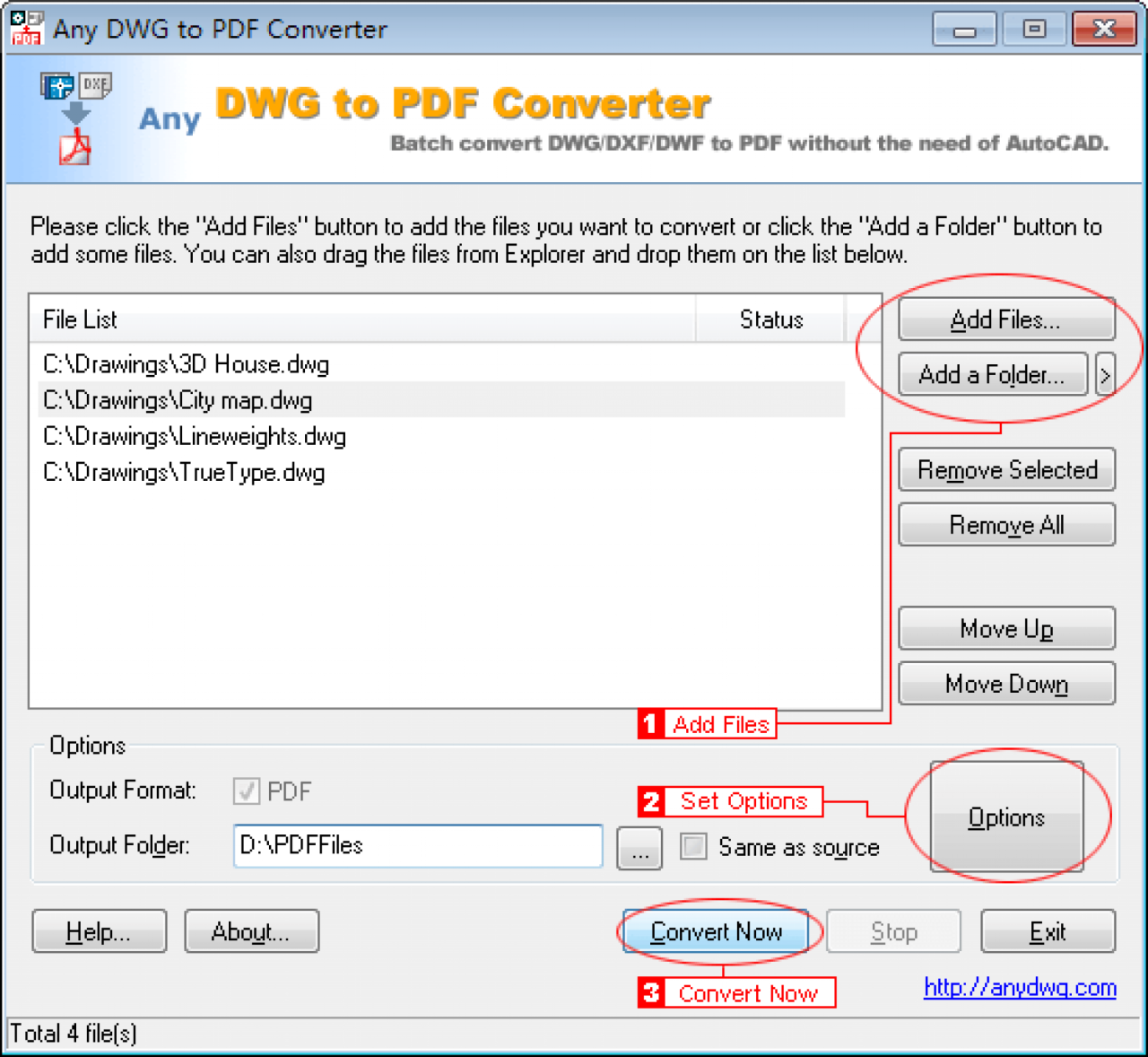
Batch Conversion
Batch conversion is a highly valuable feature in DWG converters, enabling you to convert multiple DWG files simultaneously. This saves time and effort compared to converting each file individually. Batch conversion is particularly beneficial when dealing with large projects containing numerous DWG files.
Format Support
DWG converters support various output formats, allowing you to convert DWG files to different formats like PDF, DXF, SVG, and more. The number of supported formats is an important factor to consider. Some converters support a wider range of formats, providing greater flexibility and compatibility with various applications.
Quality Preservation
Quality preservation is a critical aspect of DWG conversion. A good DWG converter should maintain the fidelity of the original DWG file, preserving the details, lines, curves, and other elements.
Other Important Features
- Preview Functionality: Some DWG converters offer preview functionality, allowing you to view the converted file before saving it. This helps ensure that the conversion has been successful and that the output file meets your requirements.
- Customization Options: Customization options, such as setting the resolution, scaling, and other parameters, provide greater control over the conversion process and allow you to tailor the output file to your specific needs.
- User Interface: A user-friendly interface simplifies the conversion process, making it easy to navigate and access the features. A clear and intuitive interface is crucial for both beginners and experienced users.
DWG Conversion Issues and Solutions
Converting DWG files can sometimes be a challenging process. Several factors can contribute to conversion errors or data loss, leading to unexpected results. Understanding common issues and their solutions is crucial for achieving accurate and reliable DWG conversions.
Conversion Errors and Data Loss
Conversion errors and data loss can occur due to various factors, including:
- File Corruption: Corrupted DWG files may contain inconsistencies or errors that can hinder conversion. This can happen due to file transfer issues, software glitches, or hardware failures.
- Version Compatibility: DWG files are associated with specific versions of AutoCAD. If the converter is not compatible with the file’s version, conversion errors can occur.
- Complex Geometry: DWG files with complex geometry, such as intricate 3D models or large datasets, may pose challenges for conversion. The converter might struggle to process and translate such complex data accurately.
- Missing Fonts or Styles: DWG files often rely on specific fonts and styles. If these elements are missing or incompatible with the target format, the converted file may display incorrectly.
- Data Loss: Conversion processes may sometimes lead to data loss. This can occur when certain features or objects are not fully supported by the target format or if the conversion settings are not properly configured.
Troubleshooting DWG Conversion Problems
Several strategies can help resolve DWG conversion issues:
- Verify File Integrity: Check the DWG file for corruption by opening it in AutoCAD or another compatible CAD program. If the file opens without errors, the issue may lie in the conversion process itself.
- Use the Latest Converter Version: Ensure you are using the latest version of the DWG converter. Updates often include bug fixes and improvements to compatibility and conversion accuracy.
- Adjust Conversion Settings: Experiment with different conversion settings to find the optimal configuration for your specific DWG file. For example, try adjusting the level of detail, the target format, or the conversion options.
- Consider Alternative Converters: If you encounter persistent conversion problems, try using a different DWG converter. Different converters may have varying levels of compatibility and features.
- Seek Technical Support: If all else fails, contact the developer of the DWG converter for technical support. They can provide assistance in diagnosing and resolving conversion issues.
Preventing Conversion Errors
Proactive measures can help minimize conversion errors:
- Save DWG Files in a Compatible Version: Save DWG files in a version that is compatible with the target format. This reduces the likelihood of conversion errors due to version incompatibility.
- Optimize DWG Files: Simplify complex geometry and remove unnecessary objects before conversion. This can improve conversion performance and reduce the risk of data loss.
- Embed Fonts and Styles: Embed fonts and styles within the DWG file to ensure they are included in the conversion process. This helps maintain the visual appearance of the converted file.
- Test Conversions: Always test conversions on a small sample of data before converting large files. This allows you to identify and address any potential issues early on.
DWG Conversion Security and Privacy
DWG files often contain sensitive information, including proprietary designs, project details, and confidential client data. When converting DWG files, it’s crucial to prioritize data security and privacy to protect this valuable information from unauthorized access or misuse.
The process of converting DWG files involves transferring data from one format to another. This process can expose your sensitive data to potential risks, especially when using online converters or sharing files over the internet. Understanding these risks and implementing appropriate security measures is essential for safeguarding your DWG files.
A DWG converter is essential for anyone working with AutoCAD files, allowing you to easily convert them to other formats. If you need to download videos from YouTube, you can use a dedicated app like the youtube video download app , which offers a convenient way to save videos for offline viewing.
Once you’ve downloaded the videos, you can use a DWG converter to create a visual representation of the data, if needed.
Security Risks Associated with Online Converters
Online DWG converters can be convenient, but they also present security risks. Here’s why:
- Data Transmission: When you upload a DWG file to an online converter, it travels over the internet, potentially exposing it to interception or unauthorized access.
- Server Security: The security of the server hosting the online converter is crucial. If the server is compromised, your DWG file could be stolen or accessed by malicious actors.
- Data Retention Policies: Some online converters may retain your uploaded DWG files on their servers, potentially exposing them to security breaches or unauthorized access.
- Third-Party Access: Online converters might share your DWG files with third-party services for processing or analysis, potentially compromising your data privacy.
Best Practices for Protecting Sensitive Data
Here are some best practices to protect your sensitive data when converting DWG files:
- Use Reputable Converters: Choose DWG converters from reputable providers with a proven track record of security and privacy. Research their security policies and practices before using their services.
- Avoid Public Wi-Fi: Avoid converting DWG files on public Wi-Fi networks, as these networks are often less secure and can expose your data to eavesdropping.
- Encrypt Your Files: Before uploading your DWG file, consider encrypting it using a strong encryption algorithm. This will make it difficult for unauthorized individuals to access your data even if it’s intercepted.
- Check Data Retention Policies: Review the data retention policies of the DWG converter you’re using. Ensure that they delete your uploaded files after conversion and have appropriate security measures in place to protect your data.
- Use Offline Converters: If you’re concerned about online security risks, consider using offline DWG converters. These converters run on your local computer and don’t require uploading your files to external servers.
The Future of DWG Conversion
The field of DWG conversion is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the changing needs of the AEC industry. Emerging trends are shaping the future of DWG conversion, promising greater efficiency, accuracy, and accessibility.
Cloud-Based Solutions, Dwg converter
Cloud-based DWG conversion solutions are gaining popularity due to their numerous advantages. These solutions offer scalability, accessibility, and affordability, making them attractive to users with varying needs.
- Scalability: Cloud-based converters can handle large volumes of data and complex DWG files without the need for expensive hardware upgrades. They can scale resources up or down as needed, ensuring optimal performance.
- Accessibility: Users can access DWG conversion services from anywhere with an internet connection, eliminating the need for local software installations.
- Affordability: Cloud-based solutions often offer subscription-based pricing models, making them more cost-effective than traditional software licenses, especially for occasional users.
Examples of popular cloud-based DWG conversion services include Autodesk’s A360 and online conversion platforms like Zamzar.
AI-Powered Converters
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing DWG conversion by enabling more accurate and intelligent conversions. AI algorithms can analyze DWG files and identify complex geometries, ensuring faithful representation of the original data.
- Enhanced Accuracy: AI-powered converters can detect and preserve intricate details, such as curves, surfaces, and complex objects, resulting in highly accurate conversions.
- Automatic Data Extraction: AI can automate the extraction of key data from DWG files, such as dimensions, material properties, and object attributes, simplifying data analysis and design workflows.
- Improved Conversion Speed: AI algorithms can optimize conversion processes, significantly reducing the time required to convert large DWG files.
Several companies are developing AI-powered DWG conversion tools, promising a future where conversions are faster, more accurate, and less prone to errors.
Evolving CAD Software and Industry Standards
The ongoing development of CAD software and industry standards will continue to impact DWG conversion. As new features and functionalities are introduced, DWG conversion tools need to adapt to ensure compatibility and accurate data transfer.
- Support for Latest CAD Versions: DWG conversion tools need to support the latest versions of AutoCAD and other CAD software to ensure seamless data exchange between different platforms.
- Compliance with Industry Standards: DWG conversion tools must comply with industry standards, such as the ISO 10303 (STEP) standard, to guarantee interoperability and data integrity.
- Integration with BIM Software: As Building Information Modeling (BIM) becomes increasingly prevalent, DWG conversion tools need to integrate with BIM software to facilitate seamless data exchange between design and construction phases.
The future of DWG conversion lies in its ability to adapt to the evolving landscape of CAD software and industry standards, ensuring data accuracy and interoperability across various platforms.
Final Review
Whether you need to convert a DWG file to a more universally compatible format like PDF, DXF, or SVG, or vice versa, a reliable DWG converter is an indispensable tool. The conversion process itself can be complex, involving different methods and considerations. Understanding the intricacies of DWG conversion and choosing the right converter for your specific needs is crucial for achieving accurate and reliable results.
