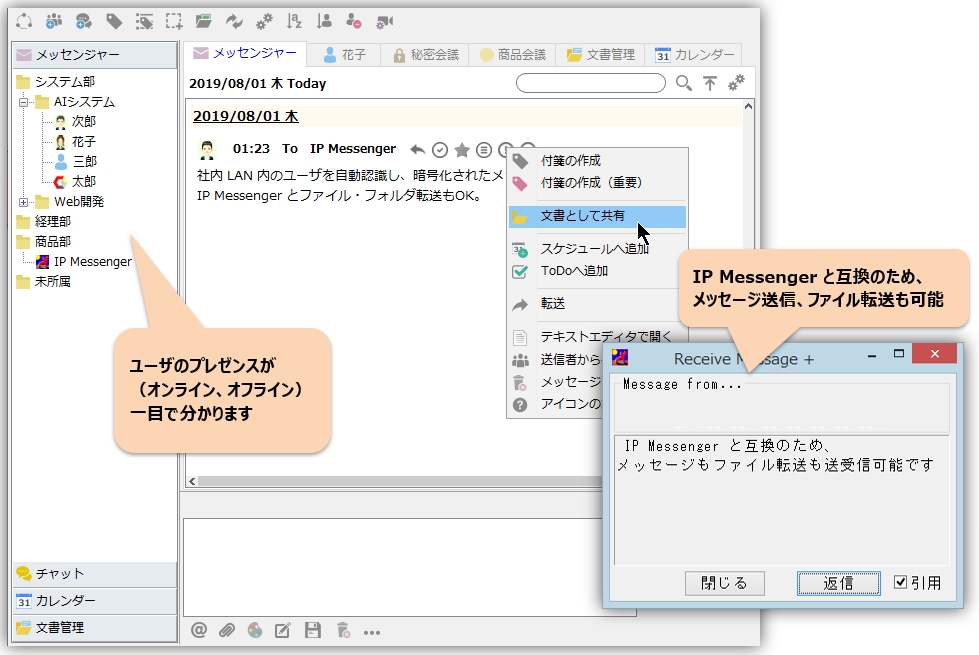
IP Messenger, a term encompassing a wide range of communication tools, has revolutionized how we connect and interact. From the early days of text-based chat to today’s multimedia-rich platforms, IP messengers have become an integral part of our digital lives.
Table of Contents
This exploration delves into the history, evolution, and impact of IP messengers, examining their technical underpinnings, social implications, and future potential. We’ll explore various types of messengers, analyze their strengths and weaknesses, and discuss the security and privacy considerations surrounding their use.
Social Impact of IP Messengers
IP messengers have revolutionized communication, profoundly impacting social interaction and communication patterns. These platforms have facilitated the formation of online communities, enabled the rise of social movements, and shaped digital culture, while also raising concerns about privacy, security, and social trust.
Impact on Social Interaction and Communication Patterns
The rise of IP messengers has led to significant shifts in how people interact and communicate. These platforms offer a convenient and accessible way to connect with others, regardless of location or time zone. This accessibility has contributed to the growth of online communities and the decline of traditional forms of communication, such as phone calls and face-to-face interactions.
- Increased Frequency of Communication: IP messengers have enabled more frequent communication among individuals, allowing for instant messaging, voice calls, and video chats. This has led to a sense of constant connectivity and the expectation of immediate responses, potentially blurring the lines between personal and professional life.
- Shifting Communication Norms: The use of emojis, GIFs, and other visual elements in IP messenger conversations has introduced new communication norms. These platforms have also fostered a more informal and casual tone in communication, which may differ from traditional written or spoken communication.
- Emergence of Online Communities: IP messengers have played a significant role in fostering online communities, providing platforms for shared interests, hobbies, and social support. These communities can connect individuals with similar backgrounds, experiences, or goals, offering a sense of belonging and shared identity.
Role in Fostering Online Communities
IP messengers have facilitated the formation of online communities by providing tools for group messaging, file sharing, and event organization. These features allow individuals to connect and collaborate with others who share similar interests, regardless of their physical location.
- Group Messaging: IP messengers offer group messaging features, enabling multiple individuals to communicate simultaneously. This facilitates the formation of online communities based on shared interests, hobbies, or professional connections.
- File Sharing: The ability to share files, photos, and videos through IP messengers allows for collaborative projects, knowledge sharing, and the creation of online communities around specific content.
- Event Organization: IP messengers often include features for organizing events, such as scheduling appointments, creating polls, and sharing location details. These features enable online communities to coordinate gatherings, workshops, and other activities.
Role in Facilitating Social Movements
IP messengers have emerged as powerful tools for facilitating social movements and political activism. Their ability to quickly disseminate information, mobilize supporters, and organize protests has contributed to the rise of digital activism and the ability of individuals to amplify their voices on a global scale.
- Rapid Information Dissemination: IP messengers enable the rapid dissemination of information, allowing individuals to share news, updates, and calls to action with a large audience. This has been crucial in mobilizing support for social movements and protests.
- Organizing and Mobilizing Supporters: Group messaging features on IP messengers allow activists to organize and mobilize supporters for protests, demonstrations, and other forms of collective action. These platforms provide a platform for coordinating efforts and sharing information among participants.
- Amplifying Voices: IP messengers have enabled individuals to amplify their voices and share their experiences with a wider audience. This has been particularly important for marginalized communities and individuals who may not have access to traditional media outlets.
Impact on Digital Culture
IP messengers have significantly shaped digital culture, influencing communication norms, social interactions, and the way information is consumed and shared. These platforms have introduced new ways of expressing oneself, connecting with others, and engaging with the digital world.
- Informal Communication: IP messengers have fostered a more informal and casual tone in communication, leading to the use of emojis, GIFs, and other visual elements. This has influenced how individuals express themselves online and how they interact with others.
- Visual Communication: The use of images, videos, and other visual content in IP messenger conversations has emphasized the importance of visual communication in digital culture. This has led to the rise of platforms like Instagram and TikTok, which focus on visual content sharing.
- Instant Gratification: IP messengers have contributed to the culture of instant gratification, where individuals expect immediate responses and access to information. This has influenced how people consume content and engage with digital platforms.
Implications for Privacy, Security, and Social Trust
While IP messengers have brought numerous benefits, they have also raised concerns about privacy, security, and social trust. These platforms collect vast amounts of data about users, including their communication history, contacts, and location information. This data can be vulnerable to breaches, misuse, and government surveillance.
- Data Privacy: IP messengers collect and store user data, including communication history, contacts, and location information. This data can be vulnerable to breaches, misuse, and government surveillance, raising concerns about user privacy.
- Security Risks: IP messengers are susceptible to security risks, such as hacking, malware, and data breaches. These risks can compromise user data, expose sensitive information, and undermine trust in the platform.
- Social Trust: The potential for misuse of user data and the spread of misinformation through IP messengers can erode social trust. This can lead to polarization, echo chambers, and a decline in the quality of public discourse.
Business Applications of IP Messengers
IP messengers have transcended their initial purpose of personal communication and have become powerful tools for businesses across various industries. Their ability to facilitate real-time, efficient, and user-friendly communication has made them indispensable for streamlining operations, enhancing customer experiences, and fostering team collaboration.
Customer Support
IP messengers offer businesses a unique opportunity to connect with their customers in a personalized and direct manner.
- Real-time Support: IP messengers enable businesses to provide immediate responses to customer inquiries, reducing wait times and enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Multi-channel Integration: Integrating IP messengers with existing customer support systems allows businesses to manage inquiries across various platforms, such as websites, social media, and email, from a single interface.
- Personalized Communication: IP messengers facilitate personalized interactions with customers, allowing businesses to address individual needs and preferences.
- Enhanced Accessibility: IP messengers are readily accessible on mobile devices, enabling businesses to reach customers anytime, anywhere.
For example, e-commerce businesses utilize IP messengers to provide instant support to customers during the checkout process, resolving issues and ensuring a smooth transaction.
Team Collaboration
IP messengers are proving to be invaluable tools for improving team communication and collaboration within organizations.
- Instant Messaging: IP messengers enable team members to communicate instantly, facilitating quick decision-making and problem-solving.
- File Sharing: Many IP messengers offer file sharing capabilities, allowing teams to share documents, presentations, and other important files seamlessly.
- Group Chat: IP messengers provide a platform for group discussions, fostering team cohesion and enabling efficient brainstorming.
- Task Management: Some IP messengers offer task management features, allowing teams to assign tasks, track progress, and collaborate on projects.
A notable example is the use of IP messengers in software development teams, where they are used for code reviews, bug reporting, and project updates.
Marketing
IP messengers have emerged as effective channels for businesses to engage with their target audience and promote their products or services.
- Targeted Messaging: IP messengers allow businesses to segment their audience and send targeted messages based on demographics, interests, and behaviors.
- Interactive Campaigns: IP messengers enable businesses to create interactive marketing campaigns, such as polls, quizzes, and contests, enhancing audience engagement.
- Promotional Offers: Businesses can leverage IP messengers to send personalized promotional offers and discounts to their customers.
- Customer Feedback: IP messengers provide a platform for businesses to gather customer feedback, enabling them to improve their products and services.
For instance, restaurants utilize IP messengers to send targeted promotions to their customers based on their past orders and preferences.
Future Trends in IP Messaging
IP messaging, as we know it, is on the cusp of a significant transformation. Emerging technologies are poised to revolutionize how we communicate, interact, and experience the digital world. From the integration of artificial intelligence to the advent of augmented reality and blockchain, these trends are set to reshape the functionalities, features, and user experience of IP messengers, ushering in a new era of communication.
Artificial Intelligence in IP Messaging
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into IP messaging platforms is poised to revolutionize user experience and communication functionalities. AI-powered features are set to enhance the efficiency, personalization, and security of IP messengers, creating a more intuitive and seamless communication experience.
- Smart Chatbots: AI-powered chatbots are revolutionizing customer service and support within IP messaging platforms. These intelligent bots can handle routine inquiries, provide personalized recommendations, and assist users with various tasks, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex issues. Examples of AI-powered chatbots in IP messaging include Facebook Messenger’s chatbot platform, which allows businesses to interact with customers directly within the messenger app, and WhatsApp’s Business API, which enables businesses to automate customer interactions and provide 24/7 support.
- Predictive Text and Automated Responses: AI algorithms can analyze user communication patterns and predict the next word or phrase, enabling faster and more efficient typing. This technology can also be used to suggest relevant responses based on the context of the conversation, streamlining communication and reducing the time spent on typing. For instance, Google’s Smart Compose feature, available in Gmail and other platforms, utilizes AI to predict and suggest words and phrases as users type, speeding up email composition.
- Enhanced Security and Privacy: AI can play a crucial role in enhancing the security and privacy of IP messaging platforms. AI-powered algorithms can detect and prevent malicious activities, such as spam, phishing attacks, and fraud, while also ensuring data privacy and confidentiality. For example, WhatsApp’s end-to-end encryption, coupled with AI-driven spam detection, helps protect user conversations from unauthorized access and malicious actors.
Augmented Reality in IP Messaging
The integration of augmented reality (AR) into IP messaging platforms is poised to transform how we communicate and interact with the digital world. AR overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing our perception and understanding of the environment around us.
- Interactive and Immersive Communication: AR can enhance communication by adding interactive elements to messaging conversations. Users can share AR experiences, such as virtual tours, product demonstrations, or interactive games, directly within the messenger app. Imagine sending a friend an AR message that allows them to virtually explore a new city or try on clothes virtually. This technology can create more engaging and memorable communication experiences.
- Contextualized Communication: AR can provide contextual information within messaging conversations. For example, imagine sending a message about a restaurant and having the AR overlay display the restaurant’s menu, reviews, and directions. This contextual information can enrich communication and make it more informative and relevant.
- Enhanced Accessibility: AR can make IP messaging platforms more accessible to users with disabilities. For instance, AR can provide real-time transcriptions of audio messages, allowing users with hearing impairments to participate in conversations.
Blockchain in IP Messaging
Blockchain technology, known for its decentralized and secure nature, has the potential to revolutionize IP messaging platforms by providing a secure and transparent platform for communication and data storage.
- Decentralized Messaging: Blockchain can enable decentralized messaging networks, eliminating the need for centralized servers and intermediaries. This can enhance privacy and security by reducing the risk of data breaches and censorship. Examples of blockchain-based messaging platforms include Telegram Open Network (TON) and Status, which aim to provide a decentralized and secure communication infrastructure.
- Secure and Tamper-Proof Communication: Blockchain’s immutability ensures that messages are tamper-proof and verifiable. This can be particularly beneficial for sensitive communications, such as financial transactions or confidential business discussions. Blockchain technology can also be used to create digital identities and verify user authenticity, reducing the risk of impersonation and fraud.
- Micropayments and Tokenized Rewards: Blockchain can facilitate micropayments and tokenized rewards within IP messaging platforms. Users can send and receive small amounts of cryptocurrency for various services, such as premium features or content creation. This can create a more engaging and rewarding user experience.
Security and Privacy Considerations
IP messengers, while offering convenient communication, come with inherent security and privacy risks. Understanding these risks and implementing appropriate safeguards is crucial for users and businesses alike.
Data Breaches
Data breaches in IP messengers can compromise sensitive information, such as personal messages, contact lists, and location data. Hackers may exploit vulnerabilities in the messenger’s software or infrastructure to gain unauthorized access to user data. Examples of such breaches include the 2017 WhatsApp vulnerability that allowed attackers to remotely install spyware on targeted devices, and the 2019 Telegram data leak that exposed user phone numbers.
Malware and Phishing Attacks
IP messengers can be a vector for malware distribution and phishing attacks. Malicious actors may send infected messages or links that, when clicked, can install malware on users’ devices or steal their credentials. Phishing attacks often mimic legitimate messages from trusted contacts or services, tricking users into revealing sensitive information.
Best Practices for Protecting User Data and Ensuring Privacy, Ip messenger
To mitigate security and privacy risks, users should adopt best practices:
- Strong Passwords: Use complex and unique passwords for each IP messenger account, avoiding easily guessable combinations.
- Encryption: Choose messengers that employ end-to-end encryption, ensuring that only the sender and receiver can access the message content.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Enable 2FA for added security, requiring an additional verification step beyond the password, such as a code sent to a mobile device.
- Regular Updates: Keep the messenger app and operating system updated to benefit from security patches and bug fixes.
- Be Cautious with Links and Attachments: Avoid clicking on suspicious links or opening attachments from unknown senders.
- Privacy Settings: Review and adjust privacy settings to control who can see your profile information, status updates, and contact list.
Regulation and Legislation
Governments and regulatory bodies are increasingly addressing security and privacy concerns related to IP messengers. Regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States impose data protection requirements on companies handling personal data, including IP messenger providers. These regulations aim to enhance user control over their data, require transparency from companies about data collection and usage, and enforce data security measures.
IP Messengers and Social Media
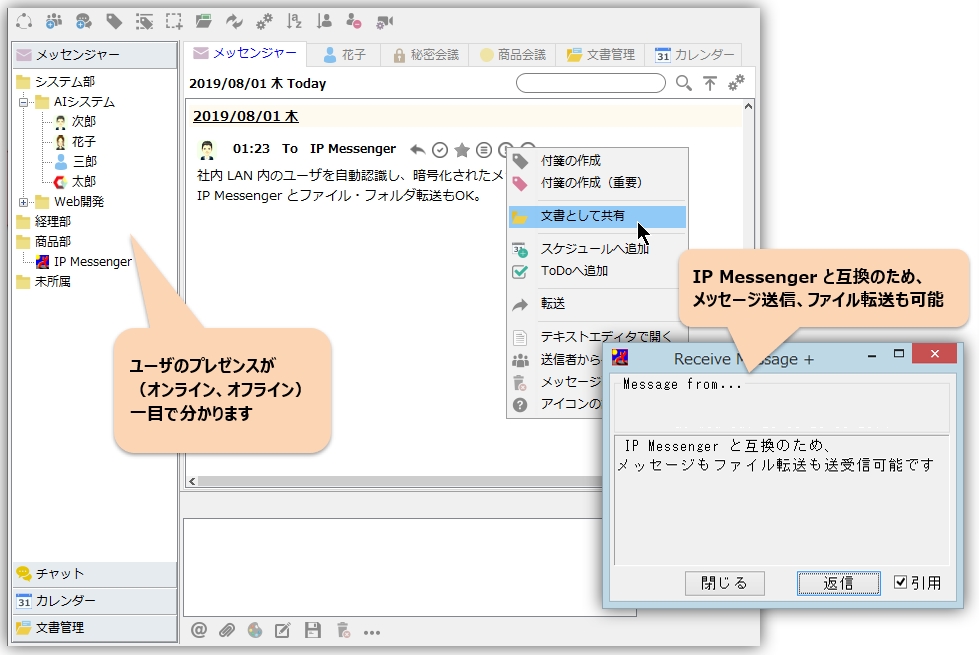
IP messengers and social media platforms are two distinct yet intertwined facets of online communication, each offering unique functionalities and user experiences. While both facilitate connecting with others, their core purposes and user interactions differ significantly. This section explores the intricate relationship between these two digital realms, examining their overlaps, distinctions, and the impact of IP messengers on the evolving landscape of social media.
The Convergence of Functionalities
IP messengers and social media platforms share common ground in their ability to connect individuals and facilitate communication. Both provide tools for sending text messages, sharing multimedia content like photos and videos, and participating in group conversations. However, their primary focus and user experiences diverge significantly.
- Instantaneous Communication: IP messengers prioritize real-time communication, emphasizing immediate delivery of messages and facilitating quick, informal interactions.
- Social Interaction and Content Sharing: Social media platforms focus on fostering social connections and sharing content with broader networks. They prioritize features like news feeds, public profiles, and content discovery algorithms, promoting broader social interactions and content dissemination.
Impact of IP Messengers on Social Media
The rise of IP messengers has profoundly influenced the evolution of social media, shaping the dynamics of online communication and user behavior.
- Shifting Communication Habits: IP messengers have become the preferred mode of communication for many, particularly younger generations. Their ease of use, privacy features, and focus on real-time interactions have led to a decline in traditional SMS messaging and a shift towards private, group-based communication.
- Emergence of Ephemeral Content: Features like disappearing messages and self-destructing content, popularized by IP messengers, have influenced social media platforms to incorporate similar features, allowing users to share content that disappears after a set time. This caters to the desire for more transient and private interactions.
- Focus on Privacy and Security: IP messengers have emphasized privacy and security features, such as end-to-end encryption and limited data collection. This has spurred social media platforms to prioritize user privacy and security measures, responding to growing concerns about data breaches and user surveillance.
Potential for Convergence and Integration
The lines between IP messengers and social media platforms are blurring as both platforms seek to enhance their functionalities and cater to evolving user needs.
- Integration of Social Features: IP messengers are incorporating social features, such as status updates, stories, and group activities, to enhance user engagement and provide a more comprehensive communication experience.
- Messenger-Based Social Networks: Some IP messengers are evolving into social networks, offering features like friend discovery, group creation, and content sharing, blurring the boundaries between messaging and social media.
- Cross-Platform Integration: Social media platforms are integrating with IP messengers, allowing users to share content and communicate directly within their social networks, creating a seamless experience across platforms.
Outcome Summary
As technology continues to advance, IP messengers are poised to play an even more significant role in shaping our communication landscape. With emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and blockchain, the future of IP messaging holds exciting possibilities, promising enhanced features, improved security, and a more personalized user experience.
IP Messenger is a great tool for instant communication, especially in a workplace setting. If you need to send a collection of documents, you can easily combine them into a single file by using a tool to merge PDF files into one.
This way, you can send a clean, organized document through IP Messenger, saving time and effort for both you and the recipient.