Remote asset monitoring solutions have revolutionized the way businesses manage their assets, offering a proactive approach to asset health and performance. These solutions leverage advanced technologies to gather real-time data from assets, enabling organizations to make informed decisions, optimize operations, and minimize downtime.
Table of Contents
From manufacturing and logistics to energy and healthcare, various industries have embraced remote asset monitoring to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve safety. This guide delves into the key components, types, benefits, challenges, and future trends of remote asset monitoring solutions, providing a comprehensive overview of this transformative technology.
Key Components of Remote Asset Monitoring Systems
Remote asset monitoring systems are designed to provide real-time insights into the performance and status of assets, regardless of their location. These systems typically consist of several key components that work together to collect, transmit, and analyze data, enabling informed decision-making and proactive maintenance.
Sensors and Data Acquisition Devices
Sensors are the foundation of any remote asset monitoring system. They are responsible for collecting data about the asset’s performance and condition. These sensors can measure various parameters, including:
- Temperature
- Pressure
- Vibration
- Flow rate
- Voltage
- Current
- Humidity
- Light intensity
The type of sensor used depends on the specific asset being monitored and the parameters that need to be tracked. For example, a temperature sensor might be used to monitor the temperature of a motor, while a vibration sensor might be used to detect early signs of bearing failure.
Data acquisition devices are responsible for collecting data from the sensors and converting it into a format that can be transmitted over a network. These devices typically have a built-in processor that can perform some basic data processing, such as filtering and averaging.
Communication Networks
Communication networks play a crucial role in transmitting data from the sensors and data acquisition devices to the monitoring platform. The choice of communication network depends on factors such as:
- Distance between the asset and the monitoring platform
- Data transmission rate
- Cost
- Security requirements
Common communication networks used in remote asset monitoring systems include:
- Cellular networks
- Satellite networks
- Wireless LAN (Wi-Fi)
- Ethernet
Cellular networks offer wide coverage and relatively low cost, making them suitable for monitoring assets in remote locations. Satellite networks are ideal for monitoring assets in areas with limited or no cellular coverage. Wireless LAN (Wi-Fi) is a cost-effective option for monitoring assets within a limited range. Ethernet is a high-speed, reliable network option for monitoring assets within a local area.
Types of Remote Asset Monitoring Solutions
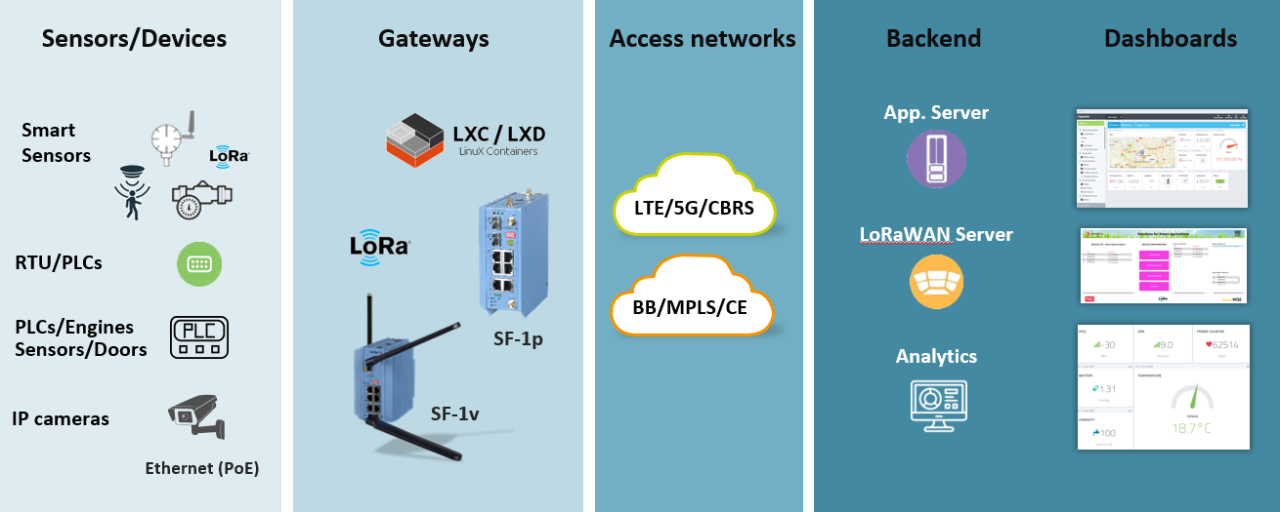
Remote asset monitoring solutions are categorized based on their functionalities and the types of data they collect and analyze. These solutions can be tailored to specific industries and asset types, offering real-time insights into asset performance, potential issues, and opportunities for optimization.
Real-Time Monitoring Solutions
Real-time monitoring solutions provide continuous updates on asset performance and operational status. These solutions are crucial for identifying immediate problems, optimizing performance, and preventing downtime.
- Data Acquisition: Real-time monitoring solutions gather data from sensors, IoT devices, and other data sources at regular intervals, often in seconds or minutes.
- Data Analysis: The collected data is analyzed in real-time using algorithms and dashboards to identify trends, anomalies, and potential issues.
- Alerts and Notifications: When predefined thresholds are exceeded or specific events occur, the system generates alerts and notifications to inform operators and maintenance personnel.
Examples:
- Industrial Machinery: Vibration sensors, temperature sensors, and pressure sensors can be used to monitor the health of critical equipment in manufacturing facilities.
- Fleet Management: GPS trackers and telematics devices provide real-time location and performance data for vehicles, enabling efficient route planning and fuel optimization.
- Energy Management: Smart meters and energy monitoring systems collect real-time energy consumption data for buildings and industrial sites, facilitating energy efficiency initiatives.
Predictive Maintenance Solutions
Predictive maintenance solutions leverage historical data and machine learning algorithms to anticipate potential failures and schedule maintenance proactively.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Predictive maintenance systems gather data from sensors, historical maintenance records, and other sources to create a comprehensive asset health profile.
- Predictive Models: Machine learning algorithms are used to develop predictive models that identify patterns and anomalies in asset performance data, indicating potential failures.
- Maintenance Scheduling: Based on the predictive models, the system recommends optimal maintenance schedules to minimize downtime and optimize asset lifespan.
Examples:
- Turbine Engines: Predictive maintenance solutions for aircraft engines analyze engine vibration, temperature, and pressure data to predict potential failures and schedule maintenance before they occur.
- Manufacturing Equipment: By monitoring vibration, temperature, and power consumption, predictive maintenance solutions can anticipate failures in critical manufacturing equipment, reducing downtime and production losses.
- Wind Turbines: Predictive maintenance solutions for wind turbines analyze wind speed, blade vibration, and gearbox temperature data to optimize performance and minimize downtime.
Asset Tracking Solutions
Asset tracking solutions provide real-time location and status updates for valuable assets, improving visibility, security, and efficiency.
- Asset Identification: Asset tracking solutions use RFID tags, GPS trackers, or other technologies to uniquely identify and track assets.
- Location Tracking: Real-time location data is provided through GPS, cellular networks, or other positioning technologies.
- Status Monitoring: Asset tracking solutions can monitor asset status, such as temperature, humidity, or movement, to ensure optimal conditions and security.
Examples:
- Supply Chain Management: Asset tracking solutions enable companies to monitor the movement of goods throughout the supply chain, improving efficiency and reducing losses.
- Fleet Management: GPS trackers provide real-time location and status updates for vehicles, improving fleet efficiency and safety.
- Equipment Rental: Asset tracking solutions allow rental companies to monitor the location and status of rented equipment, ensuring timely returns and preventing theft.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
The collected data from remote asset monitoring systems is useless without proper analysis and interpretation. This process helps extract valuable insights, enabling informed decision-making and optimizing asset performance.
Data Analysis Methods
Data analysis techniques play a crucial role in extracting meaningful information from the collected data. Various methods are employed, including:
- Statistical Analysis: This method involves using statistical techniques like mean, median, standard deviation, and regression analysis to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies in the data. For example, analyzing historical temperature data of a server room can reveal potential overheating issues and help predict future failures.
- Machine Learning: Advanced algorithms are used to identify patterns and predict future behavior based on historical data. This is particularly useful for predictive maintenance, where algorithms can identify potential failures before they occur. For example, a machine learning model trained on vibration data from a pump can predict its remaining useful life and schedule maintenance proactively.
- Data Visualization: This method uses charts, graphs, and dashboards to present data in a visually appealing and easily understandable manner. This helps identify trends, patterns, and outliers quickly and efficiently. For example, a dashboard displaying real-time sensor data from a fleet of vehicles can quickly highlight vehicles exceeding speed limits or experiencing engine problems.
Dashboards and Visualizations
Dashboards and visualizations are essential tools for presenting data insights to stakeholders. They provide a clear and concise overview of asset performance, enabling quick identification of potential issues and facilitating informed decision-making.
- Real-time Data Visualization: Dashboards can display real-time data from sensors, providing a live view of asset performance. This allows for immediate detection of issues and prompt intervention. For example, a dashboard showing the real-time temperature and humidity levels of a warehouse can alert operators to potential environmental issues affecting stored goods.
- Trend Analysis: Dashboards can also display historical data trends, helping identify patterns and predict future behavior. This allows for proactive maintenance and optimization of asset performance. For example, a dashboard showing historical energy consumption data of a building can identify periods of high energy usage and help implement energy-saving measures.
- Alerts and Notifications: Dashboards can be configured to send alerts and notifications when predefined thresholds are exceeded. This ensures timely intervention and prevents potential problems from escalating. For example, a dashboard monitoring the pressure levels of a pipeline can send alerts when pressure drops below a critical level, preventing potential leaks and safety hazards.
Identifying Potential Issues
Data analysis can effectively identify potential issues and prevent costly downtime. By analyzing historical data and identifying patterns, potential problems can be anticipated and addressed before they escalate.
- Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing historical data, machine learning algorithms can predict the likelihood of future failures. This allows for proactive maintenance, reducing downtime and extending asset life. For example, a machine learning model trained on vibration data from a wind turbine can predict potential bearing failures, enabling scheduled maintenance before the turbine fails.
- Anomaly Detection: Data analysis techniques can identify unusual patterns and anomalies in asset behavior, indicating potential issues. For example, analyzing sensor data from a manufacturing machine can identify unexpected vibrations or temperature fluctuations, signaling potential malfunctions.
- Performance Degradation: By tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), data analysis can identify gradual performance degradation and alert operators to potential issues. For example, analyzing the fuel efficiency of a fleet of vehicles can identify vehicles with declining performance, indicating potential mechanical problems.
Optimizing Asset Performance
Data analysis can be used to optimize asset performance and improve efficiency. By identifying areas for improvement, organizations can maximize asset utilization and reduce operational costs.
- Resource Optimization: Data analysis can identify areas where resources are being overused or underutilized. This allows for better allocation of resources and improved efficiency. For example, analyzing energy consumption data from a factory can identify periods of low utilization, enabling optimization of production schedules and reducing energy costs.
- Process Optimization: Data analysis can identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies in processes. This allows for process improvements and optimization, leading to increased productivity and reduced costs. For example, analyzing data from a supply chain can identify delays and inefficiencies, enabling process optimization and improved logistics.
- Performance Benchmarking: Data analysis can be used to benchmark asset performance against industry standards. This allows for identifying areas for improvement and achieving best-in-class performance. For example, analyzing the uptime of a fleet of trucks against industry averages can identify areas for improvement and optimize maintenance strategies.
Improving Decision-Making
Data analysis provides valuable insights that support informed decision-making. By leveraging data-driven insights, organizations can make more strategic decisions, improve operational efficiency, and enhance asset performance.
- Data-Driven Insights: Data analysis provides objective insights, reducing reliance on intuition and subjective opinions. This leads to more informed and data-backed decisions. For example, analyzing historical data on customer service calls can identify common issues and inform the development of targeted training programs for customer service representatives.
- Risk Mitigation: Data analysis can identify potential risks and vulnerabilities, enabling proactive mitigation strategies. This reduces the likelihood of unexpected events and minimizes potential downtime. For example, analyzing data from a building’s security system can identify patterns of suspicious activity, enabling security personnel to take preventative measures.
- Strategic Planning: Data analysis can support strategic planning by providing insights into market trends, customer behavior, and asset performance. This allows organizations to make informed decisions about future investments, resource allocation, and product development. For example, analyzing data on customer preferences can inform the development of new products and services, ensuring they meet market demands.
Benefits of Remote Asset Monitoring: Remote Asset Monitoring Solutions
Remote asset monitoring solutions offer a wide range of advantages that can significantly improve the efficiency and profitability of businesses across various industries. By leveraging real-time data and advanced analytics, these solutions empower organizations to optimize asset performance, reduce operational costs, and enhance overall business outcomes.
Economic Benefits
Remote asset monitoring solutions can deliver significant economic benefits by reducing downtime and maintenance costs, enhancing asset efficiency, and improving productivity. These solutions enable organizations to proactively identify and address potential issues before they escalate into costly breakdowns.
- Reduced Downtime: By monitoring assets in real-time, organizations can detect anomalies and potential failures early on, allowing for timely interventions and minimizing downtime. This is crucial for businesses where even short periods of downtime can result in significant financial losses.
- Lower Maintenance Costs: Predictive maintenance, enabled by remote asset monitoring, allows organizations to schedule maintenance tasks based on actual asset conditions rather than fixed intervals. This helps prevent unnecessary maintenance and extends the lifespan of assets, leading to substantial cost savings.
- Increased Asset Efficiency: By analyzing data from remote sensors, organizations can gain insights into asset performance and identify areas for improvement. This allows them to optimize asset utilization, reduce energy consumption, and maximize productivity.
Improved Asset Efficiency and Productivity
Remote asset monitoring empowers organizations to optimize asset performance and enhance productivity by providing real-time insights into asset operations. By analyzing data collected from sensors, organizations can identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to maximize asset utilization.
- Real-Time Performance Monitoring: Remote monitoring solutions provide continuous visibility into asset performance, allowing organizations to track key metrics such as temperature, vibration, and pressure. This real-time data enables proactive identification of potential issues and optimization of asset operations.
- Optimized Asset Utilization: By analyzing asset performance data, organizations can identify underutilized assets and implement strategies to maximize their utilization. This can lead to increased production output and improved overall efficiency.
- Enhanced Asset Lifespan: Predictive maintenance, enabled by remote asset monitoring, allows organizations to identify and address potential issues before they escalate into major failures. This helps extend the lifespan of assets and reduces the need for premature replacements.
Real-World Examples
Remote asset monitoring solutions have proven to be highly effective in various industries, delivering tangible benefits and achieving specific goals. Here are some examples:
- Manufacturing: A manufacturing company implemented a remote asset monitoring solution to track the performance of its production machinery. The solution provided real-time data on equipment health, enabling the company to identify and address potential issues before they led to downtime. This resulted in a significant reduction in maintenance costs and increased production efficiency.
- Energy: An energy company deployed remote asset monitoring to monitor the performance of its wind turbines. The solution provided data on wind speed, turbine RPM, and power output, enabling the company to optimize turbine operation and maximize energy production. This resulted in increased energy efficiency and reduced operational costs.
- Transportation: A transportation company used remote asset monitoring to track the location and performance of its fleet of trucks. The solution provided real-time data on fuel consumption, engine performance, and driver behavior, enabling the company to optimize route planning, reduce fuel consumption, and improve driver safety. This resulted in significant cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
Challenges and Considerations
Implementing a remote asset monitoring system can be a complex process with various challenges and considerations. It’s crucial to carefully assess these aspects to ensure a successful and effective deployment.
Data Security and Privacy
Data security and privacy are paramount in remote asset monitoring. Sensitive information about assets and operations is collected and transmitted, making it vulnerable to unauthorized access or breaches.
- Data Encryption: Implementing strong encryption protocols for data transmission and storage is essential. This protects sensitive information from unauthorized access, even if intercepted. For example, using Transport Layer Security (TLS) or Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) for data transmission and encrypting data at rest using advanced algorithms like AES-256.
- Access Control: Implementing robust access control measures is crucial. This involves limiting access to data based on user roles and permissions. This ensures that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information. For example, using multi-factor authentication (MFA) for user logins and implementing role-based access control (RBAC) to restrict access to specific data sets.
- Data Compliance: Adhering to relevant data privacy regulations is essential. Depending on the industry and location, organizations must comply with regulations like GDPR, CCPA, or HIPAA. This ensures that data is collected, processed, and stored legally and ethically. For example, organizations should implement data retention policies, data anonymization techniques, and procedures for handling data breaches.
Selecting the Right Solution
Choosing the right remote asset monitoring solution is crucial for success. This involves considering various factors, including budget constraints, specific needs, and scalability.
- Budget: Remote asset monitoring solutions can range in cost from basic, cost-effective options to sophisticated, enterprise-grade systems. Organizations must carefully evaluate their budget and choose a solution that aligns with their financial constraints. For example, smaller businesses might opt for cloud-based solutions with subscription models, while larger enterprises might invest in on-premise systems with higher upfront costs.
- Specific Needs: The specific needs of the organization will determine the features and functionalities required in a remote asset monitoring solution. Factors like the type of assets being monitored, the required data granularity, and the desired level of automation will influence the choice. For example, a company monitoring high-value equipment might require a solution with real-time data streaming and advanced analytics, while a company monitoring basic assets might only need a solution with basic monitoring and reporting capabilities.
- Scalability: As organizations grow and their asset portfolio expands, the remote asset monitoring solution should be scalable to accommodate the increased data volume and complexity. This involves considering factors like the solution’s ability to handle large amounts of data, the ease of adding new assets, and the flexibility to adapt to future requirements. For example, a cloud-based solution with elastic scalability can easily adapt to changing needs, while an on-premise solution might require significant infrastructure upgrades for scaling.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Remote asset monitoring solutions have proven their value across diverse industries, offering tangible benefits and driving significant improvements. This section delves into real-world case studies showcasing the successful implementation of these solutions, highlighting the challenges faced, solutions adopted, and positive outcomes achieved. By examining these examples, we gain valuable insights into best practices and lessons learned from industry experts.
Success Story: Optimizing Oil and Gas Operations, Remote asset monitoring solutions
This case study focuses on a leading oil and gas company that implemented a comprehensive remote asset monitoring solution to enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
The company faced several challenges, including:
- Frequent equipment failures leading to production disruptions.
- Difficulty in identifying potential issues early.
- Limited access to real-time data for informed decision-making.
To address these challenges, the company deployed a remote asset monitoring system that integrated sensors, data analytics, and remote access capabilities. This system enabled:
- Real-time monitoring of critical equipment parameters.
- Early detection of anomalies and potential failures.
- Predictive maintenance planning to minimize downtime.
- Remote troubleshooting and support for faster resolution of issues.
The implementation of this solution resulted in:
- A significant reduction in equipment failures and downtime.
- Improved operational efficiency and productivity.
- Enhanced safety through early detection of potential hazards.
- Reduced maintenance costs and increased asset lifespan.
“The remote asset monitoring solution has revolutionized our operations, allowing us to proactively address potential issues before they escalate into major problems. This has significantly reduced downtime, improved safety, and boosted our overall efficiency.” – [Name], Operations Manager, [Company Name]
Success Story: Enhancing Efficiency in Manufacturing
This case study explores how a manufacturing company leveraged remote asset monitoring to streamline production processes and optimize resource utilization.
The company faced challenges such as:
- Inefficient production scheduling and resource allocation.
- Lack of real-time visibility into production performance.
- Difficulty in identifying bottlenecks and optimizing workflows.
The company implemented a remote asset monitoring system that provided real-time data on production line performance, equipment status, and material flow. This enabled:
- Real-time monitoring of production processes and key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Data-driven optimization of production schedules and resource allocation.
- Identification of bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
- Improved communication and collaboration among production teams.
The implementation of this solution led to:
- Increased production efficiency and output.
- Reduced production costs and waste.
- Improved product quality and consistency.
- Enhanced responsiveness to changing market demands.
“The remote asset monitoring system has provided us with the real-time insights we needed to optimize our production processes. We have seen significant improvements in efficiency, quality, and cost savings.” – [Name], Production Manager, [Company Name]
Future Trends in Remote Asset Monitoring
The field of remote asset monitoring is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing demand for efficient and data-driven asset management. Emerging technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) are playing a pivotal role in shaping the future of remote asset monitoring solutions.
Impact of IoT and AI on Remote Asset Monitoring
The integration of IoT and AI is revolutionizing remote asset monitoring by enabling real-time data collection, sophisticated analytics, and proactive maintenance strategies.
- Real-time Data Collection: IoT devices equipped with sensors can collect vast amounts of data from assets, providing real-time insights into their performance and health. This data can be used to identify potential problems before they escalate, leading to improved asset uptime and reduced maintenance costs.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms can analyze historical data and real-time sensor readings to predict potential failures and schedule maintenance proactively. This approach helps prevent costly downtime and ensures optimal asset performance.
- Remote Asset Optimization: AI-powered analytics can optimize asset utilization and efficiency by identifying patterns and trends in asset performance data. This data can be used to adjust operating parameters, optimize maintenance schedules, and improve overall asset management practices.
Future Directions of Remote Asset Monitoring
The future of remote asset monitoring is characterized by increasing sophistication and integration with other technologies.
- Cloud-Based Platforms: Cloud-based platforms will become increasingly prevalent, offering scalable and cost-effective solutions for data storage, analysis, and visualization. These platforms will enable real-time monitoring and collaboration among stakeholders.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing will play a crucial role in processing data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving real-time decision-making capabilities. This approach is particularly beneficial for applications requiring rapid response times, such as predictive maintenance.
- Digital Twins: Digital twins, virtual representations of physical assets, will become increasingly sophisticated, allowing for detailed simulations and analysis of asset performance under different conditions. This technology will enable more accurate predictions and proactive maintenance strategies.
Applications of Remote Asset Monitoring
Remote asset monitoring solutions are finding applications across various industries, including:
- Manufacturing: Monitoring equipment performance, identifying potential failures, and optimizing production processes.
- Energy: Monitoring power grids, wind turbines, and solar farms for efficiency and reliability.
- Transportation: Monitoring vehicle performance, optimizing routes, and reducing fuel consumption.
- Healthcare: Monitoring medical equipment, ensuring patient safety, and optimizing resource allocation.
Implementation Considerations
Implementing a remote asset monitoring system requires careful planning and consideration of various factors. This section delves into crucial aspects to ensure a successful deployment.
Choosing the Right Technology
The selection of appropriate technology is paramount for a successful remote asset monitoring system. This involves considering factors such as:
- Type of assets being monitored: Different assets require different types of sensors and communication protocols. For example, monitoring temperature in a refrigerator requires a different sensor than monitoring vibration in a motor.
- Environmental conditions: The environment where the assets are located can impact the choice of technology. For example, sensors deployed in harsh environments require robust construction and protection from extreme temperatures or moisture.
- Data requirements: The frequency and accuracy of data collection are crucial considerations. High-frequency data collection may require more bandwidth and processing power, while low-frequency data collection may be sufficient for some applications.
- Budget constraints: The cost of hardware, software, and installation can vary significantly. It’s essential to choose a solution that fits within the allocated budget.
Security and Data Privacy
Data security and privacy are critical concerns in remote asset monitoring. It’s essential to implement measures to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and cyber threats. This includes:
- Secure communication protocols: Utilizing encryption and authentication protocols ensures secure data transmission between sensors and the monitoring platform.
- Access control: Restricting access to the monitoring system to authorized personnel helps prevent unauthorized data access.
- Data backups and disaster recovery: Implementing data backups and disaster recovery plans safeguards against data loss due to hardware failures or cyberattacks.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating the remote asset monitoring system with existing enterprise systems, such as ERP or SCADA, can enhance data flow and streamline operations. This integration allows for:
- Real-time data sharing: Seamlessly integrating data from the monitoring system with other systems provides a unified view of asset performance.
- Automated alerts and notifications: Integrating with existing systems enables automated alerts and notifications based on predefined thresholds or events, triggering appropriate actions.
- Data analysis and reporting: Combining data from multiple sources provides comprehensive insights into asset performance and facilitates data-driven decision-making.
Training and Support
Providing adequate training and support to personnel responsible for managing and operating the remote asset monitoring system is crucial for its effective implementation. This includes:
- Technical training: Training on the system’s hardware, software, and configuration ensures users can effectively operate and troubleshoot the system.
- Data interpretation and analysis: Training on data interpretation and analysis enables users to extract meaningful insights from the collected data.
- Ongoing support: Providing ongoing support through documentation, FAQs, and technical assistance ensures users have the necessary resources to address any challenges or questions.
Final Thoughts

As the landscape of asset management continues to evolve, remote asset monitoring solutions are poised to play an even more critical role. By harnessing the power of data analytics, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things, organizations can unlock new levels of asset visibility, predictive maintenance, and operational excellence. The future of asset management is connected, intelligent, and data-driven, with remote monitoring at the forefront of this transformation.
Remote asset monitoring solutions are vital for businesses to keep track of their equipment and ensure optimal performance. Often, reports and documentation related to these solutions are provided in PDF format. To easily edit and integrate this information into other systems, you might find a pdf to doc converter online helpful.
This tool allows you to convert PDF files into editable Word documents, streamlining the process of analyzing data and making informed decisions regarding your remote asset monitoring strategy.
