RMM server sets the stage for a streamlined and efficient IT management approach, offering a centralized platform for monitoring, managing, and securing your devices. Imagine a world where you can remotely access and control your computers, deploy software updates, and proactively identify potential security threats, all from a single, intuitive interface.
Table of Contents
This technology empowers IT professionals to manage their infrastructure effectively, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity. Whether you’re a small business owner or a large enterprise, an RMM server can be a game-changer for your IT operations.
What is RMM Server?
An RMM server, or Remote Monitoring and Management server, is a powerful tool used by IT professionals to manage and monitor computer systems remotely. It provides a centralized platform for managing a wide range of tasks, from software updates and security patches to system performance monitoring and troubleshooting.
Key Functions and Features of an RMM Server
RMM servers offer a comprehensive set of features that streamline IT management and enhance security. These include:
- Remote Control and Access: RMM servers allow IT professionals to access and control devices remotely, enabling them to troubleshoot issues, install software, or perform other administrative tasks without physically being present at the device location.
- Software Deployment and Patch Management: RMM servers facilitate the automated deployment of software updates and security patches across multiple devices, ensuring that all systems are up-to-date and protected against vulnerabilities.
- System Monitoring and Reporting: RMM servers continuously monitor system performance, hardware health, and security status, providing real-time insights and generating detailed reports to identify potential issues and trends.
- Asset Management: RMM servers enable IT professionals to track and manage all IT assets, including hardware, software, and licenses, providing a comprehensive inventory and simplifying asset management tasks.
- Security and Compliance: RMM servers offer advanced security features, such as endpoint protection, firewall management, and data encryption, to protect devices and sensitive information from threats.
Benefits of Using an RMM Server for IT Management
Implementing an RMM server offers numerous benefits for IT departments, including:
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: RMM servers automate many routine IT tasks, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives and complex problems.
- Enhanced Security and Compliance: RMM servers provide comprehensive security measures, ensuring that devices are protected from threats and meet compliance requirements.
- Reduced Downtime and Improved Performance: RMM servers enable proactive monitoring and troubleshooting, minimizing downtime and improving overall system performance.
- Cost Savings: RMM servers can help reduce IT costs by automating tasks, minimizing downtime, and improving efficiency.
- Scalability and Flexibility: RMM servers can scale to accommodate the needs of organizations of all sizes, providing a flexible and adaptable solution for IT management.
Types of RMM Servers
RMM servers come in various forms, each catering to specific needs and target audiences. Understanding the different types of RMM servers can help you choose the best solution for your organization.
Categorizing RMM Servers
RMM servers can be categorized based on their functionality and target audience. The following are the primary categories:
- On-Premise RMM Servers: These servers are physically located within an organization’s data center or network. They provide greater control and security, as the organization has complete ownership and management of the server infrastructure. However, they require significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance.
- Cloud-Based RMM Servers: These servers are hosted in a cloud environment, allowing for accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection. They offer flexibility, scalability, and reduced infrastructure costs. However, organizations relinquish some control over data security and server configuration.
- Hybrid RMM Servers: These servers combine the features of on-premise and cloud-based solutions, offering a balance of control and flexibility. Organizations can choose to host specific services on-premise while leveraging the cloud for other functionalities.
Advantages and Disadvantages of RMM Server Types
The following table summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of each type of RMM server:
| Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| On-Premise |
|
|
| Cloud-Based |
|
|
| Hybrid |
|
|
Examples of Popular RMM Server Solutions
Here are some examples of popular RMM server solutions and their key features:
- ConnectWise Automate: A comprehensive RMM solution offering remote monitoring, management, and automation capabilities. It supports both on-premise and cloud deployments. Key features include patch management, software distribution, and endpoint security.
- Datto RMM: A cloud-based RMM solution focused on MSPs (Managed Service Providers). It offers comprehensive remote management, security, and automation tools. Key features include endpoint security, backup and disaster recovery, and automated scripting.
- NinjaOne: A cloud-based RMM solution designed for small and medium-sized businesses. It provides remote monitoring, management, and automation capabilities, with a focus on ease of use and affordability. Key features include endpoint security, patch management, and automated scripting.
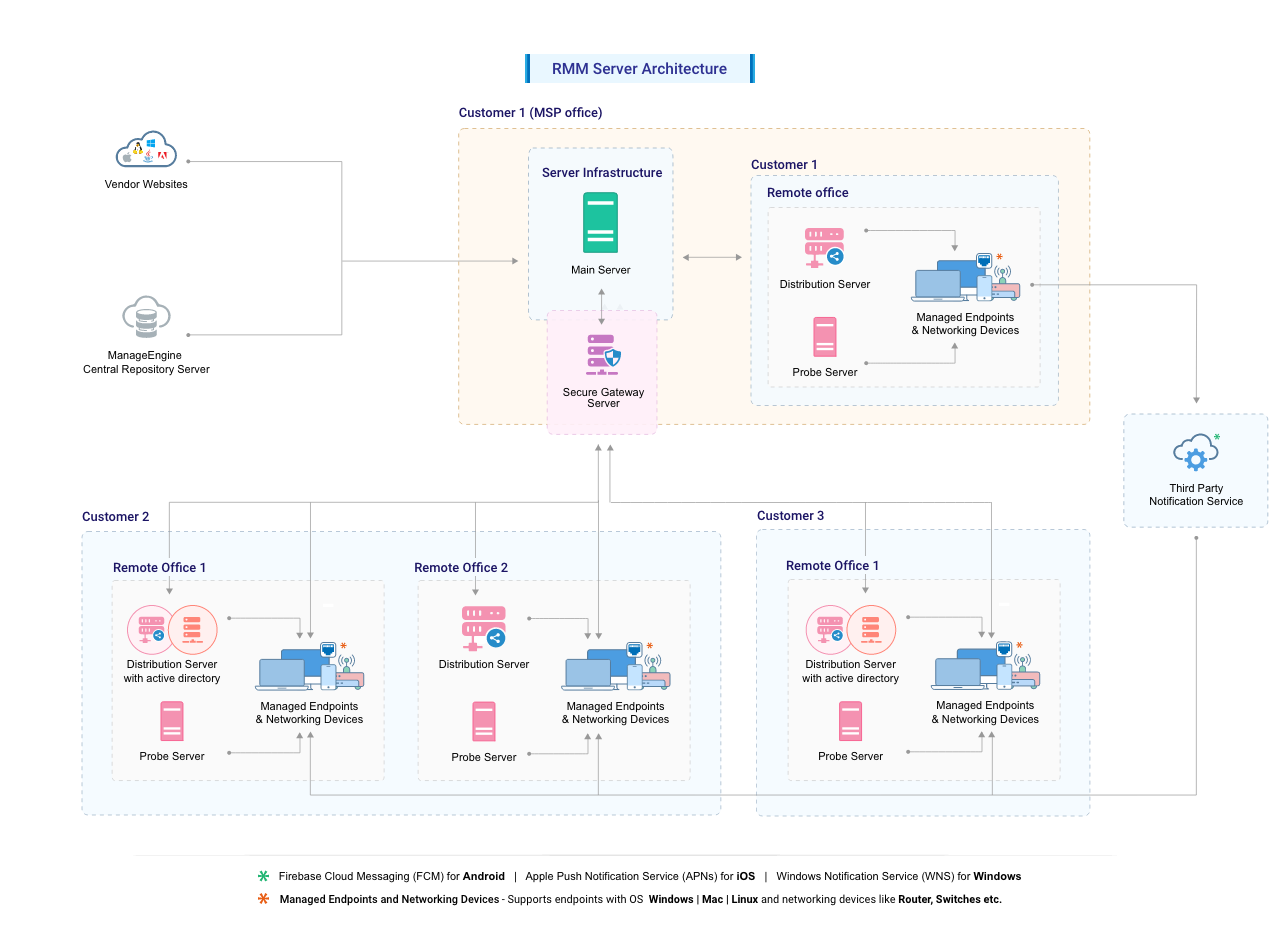
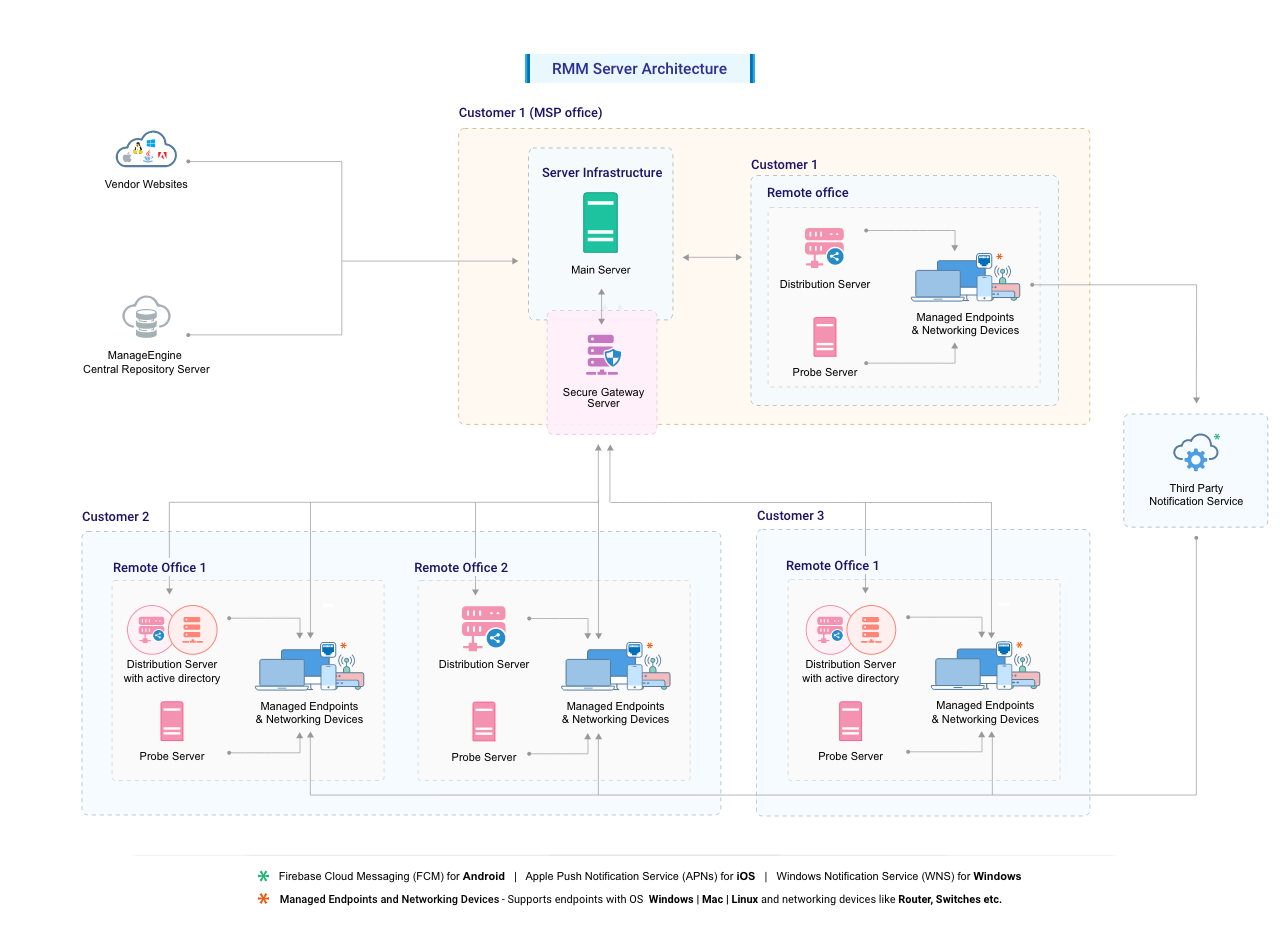
RMM Server Architecture
An RMM server’s architecture is designed to manage and monitor devices remotely. This architecture involves various components that work together to ensure efficient operation and data collection.
Components and Roles
The architecture of an RMM server typically consists of the following key components:
- RMM Server: The central hub of the RMM system, responsible for managing and monitoring devices. It acts as the central control point, collecting data from managed devices and providing administrative functions.
- Agent: Software installed on each managed device, responsible for communicating with the RMM server. It gathers data about the device’s hardware, software, and security status, and sends it back to the server for analysis.
- Database: Stores all collected data from managed devices. This data includes device inventory, software updates, security vulnerabilities, and system performance metrics. It allows for historical analysis and reporting.
- Management Console: A web-based interface that allows administrators to access and manage the RMM server. It provides features for configuring policies, monitoring devices, running scripts, and deploying software updates.
- Reporting Engine: Generates reports based on collected data. This includes device health summaries, security vulnerability reports, and performance metrics, enabling administrators to gain insights into the overall health and security of their managed devices.
Data Collection and Interaction
The RMM server interacts with managed devices through the agent software. The agent collects data from the device and sends it to the server using various communication protocols, such as TCP/IP or HTTPS.
The data collected includes:
- Hardware Information: CPU, RAM, storage, network interfaces, etc.
- Software Inventory: Operating system, applications, drivers, etc.
- Security Status: Antivirus, firewall, and other security software configurations.
- System Performance: CPU utilization, memory usage, disk space, etc.
- Event Logs: System events, errors, and warnings.
Security Considerations
The security of an RMM server is crucial, as it manages sensitive data from multiple devices. Here are some key security considerations:
- Secure Communication: Employ strong encryption protocols like HTTPS to protect data transmitted between the server and agents.
- Access Control: Implement robust user authentication and authorization mechanisms to restrict access to the RMM server and its data.
- Agent Security: Ensure that the agents installed on managed devices are secure and regularly updated to prevent vulnerabilities.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities in the RMM server and its components.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Implement a comprehensive data backup and recovery plan to protect the RMM server’s data from loss or corruption.
RMM Server Deployment and Configuration
Deploying and configuring an RMM server involves setting up the server software, installing agents on managed devices, and configuring policies and settings for remote management. This process ensures that the server can effectively monitor, manage, and protect the network and its connected devices.
Installing the RMM Server Software
The initial step in deploying an RMM server is installing the server software. This process typically involves downloading the software from the vendor’s website, running the installation wizard, and configuring basic settings like server name, database details, and network settings.
- Download the RMM Server Software: Download the latest version of the RMM server software from the vendor’s website. Ensure the software is compatible with your operating system and network infrastructure.
- Run the Installation Wizard: Execute the installation file and follow the on-screen instructions. This usually involves accepting the license agreement, choosing an installation directory, and configuring basic settings.
- Configure Basic Settings: During installation, configure essential settings such as the server name, database details, network settings, and user accounts. These settings are crucial for the server’s functionality and access control.
Installing Agents on Managed Devices
Once the RMM server is installed, the next step is to install agents on the managed devices. These agents act as the communication bridge between the server and the devices, allowing for remote monitoring and management.
- Agent Deployment Methods: Agents can be deployed using various methods, including manual installation, automated deployment using scripts or group policies, or through the RMM server’s built-in deployment tools.
- Agent Configuration: After installation, agents need to be configured to connect to the RMM server and specify the level of monitoring and management required. This involves setting up communication protocols, authentication credentials, and reporting frequency.
Configuring Policies and Settings
The final step in RMM server deployment is configuring policies and settings for remote management. These policies define the rules and parameters for how the server interacts with managed devices, ensuring consistent and effective management.
- Security Policies: Implement security policies to control access to managed devices, enforce password complexity, and restrict unauthorized software installations. These policies protect devices from security threats and ensure data integrity.
- Monitoring Policies: Configure monitoring policies to define what data is collected from managed devices, the frequency of collection, and the thresholds for triggering alerts. These policies ensure that the server can proactively identify and address potential issues.
- Management Policies: Establish management policies to define the level of control the server has over managed devices, including software updates, patch management, and remote access permissions. These policies streamline device management and ensure compliance with security best practices.
RMM Server Management and Maintenance
An RMM server, like any other critical infrastructure, requires ongoing management and maintenance to ensure its optimal performance, security, and reliability. This section explores the essential tasks involved in managing and maintaining an RMM server.
Monitoring Server Performance and Resource Utilization
Monitoring server performance and resource utilization is crucial for identifying potential issues and ensuring the smooth operation of the RMM server. This includes monitoring key metrics like CPU usage, memory consumption, disk space, and network traffic.
- CPU Usage: Monitoring CPU usage helps identify potential bottlenecks and ensure that the server has sufficient processing power to handle its workload. High CPU usage can indicate issues like resource-intensive tasks, malware infections, or inefficient code.
- Memory Consumption: Keeping an eye on memory usage is essential for preventing performance degradation and system crashes. High memory consumption can indicate memory leaks, resource-intensive applications, or insufficient RAM.
- Disk Space: Monitoring disk space helps prevent the server from running out of storage, which can lead to data loss or application failures. It’s important to monitor both free space and disk usage patterns.
- Network Traffic: Monitoring network traffic helps identify potential security threats, performance bottlenecks, and bandwidth usage patterns. High network traffic can indicate DDoS attacks, malware infections, or excessive data transfers.
Performing Regular Backups and Updates
Regular backups and updates are essential for protecting data and ensuring the security and stability of the RMM server.
- Backups: Regular backups create copies of critical data and configurations, allowing for data recovery in case of hardware failures, software errors, or cyberattacks. Backups should be stored securely off-site to prevent data loss in the event of a disaster.
- Updates: Software updates often include security patches, bug fixes, and performance enhancements. Regularly updating the RMM server and its components helps protect against vulnerabilities and ensures optimal performance.
Maintaining Server Security
Maintaining server security is paramount to protecting sensitive data and ensuring the integrity of the RMM system.
- Firewall: A firewall acts as a barrier between the server and the external network, blocking unauthorized access and malicious traffic. It’s essential to configure the firewall to allow only necessary traffic and block all other connections.
- Antivirus Software: Antivirus software protects the server from malware infections, which can compromise data security and server performance. Regularly updating antivirus software ensures it can detect and remove the latest threats.
- User Account Management: Implementing strong password policies and limiting user access to only necessary resources helps prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Regularly review user accounts and permissions to ensure security.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular security audits helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the server’s security posture. These audits can include penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and log analysis.
Summary
As the IT landscape continues to evolve, RMM servers are becoming increasingly essential for businesses of all sizes. Their ability to automate tasks, enhance security, and provide real-time insights makes them a powerful tool for managing your technology infrastructure. By embracing RMM server solutions, you can unlock a new level of efficiency, security, and control over your IT environment.
An RMM server is a powerful tool for managing and monitoring your devices, but it’s crucial to ensure your systems are running smoothly. If you encounter an error like a missing operating system , your RMM server might struggle to connect and perform its tasks.
Fortunately, most RMM servers have built-in tools to diagnose and resolve these issues, allowing you to quickly get your systems back online.